Guidance of Hydra Deployment and RPC Settings
This guidance includes how to deploy, run and make RPC calls.
Suppose the readers are able to use Linux,Mac or Windows command line. If you are not familiar with command line, or just interested in using GUI wallet, please refer to another document about hydra Wallet Tutorial.
Get hydra Node
There are at least 4 ways to get a hydra node, you can choose any way:
1. Download the binaries
If you do not care much about hydra's source code, the easiest way to obtain hydra node is to download the latest binaries on the hydra release page. Currently it supports Linux, Window, OSX. It is highly recommended to download the latest version. In this guidance, we will use v0.20.12 version as an example。
(Note: the version number you see might be different, here is v0.20.12, but other key words except for version are the same.)
For Mac user:hydra-0.20.18-macos.dmg
For Linux users: hydra-0.20.18-ubuntu20.04-x86_64-gnu.zip or hydra-0.20.18-ubuntu18.04-x86_64-gnu.zip
For Windows users:hydra-0.20.18-win64.zip or hydra-0.20.18-win32.zip
For Raspberry Pi:hydra-0.20.18-aarch64-linux-gnu.zip (for Bookworm64 and Bullseye64) or hydra-0.20.18-arm-linux-gnueabihf.zip (for Bookworm32 and Bullseye32)
Decompress after downloading, then you will get hydrad and hydra-cli under the path/bin.
Please refer to https://github.com/Hydra-Chain/node/releases,Current support Ubuntu,Debian and Mint。
Raspberry Pi users can also use apt - please refer to https://github.com/Hydra-Chain/node/releases
After installation, you should be able to run hydrad and hydra-clidirectly in the terminal。
2. Compiler from source code
If you want to compile latest hydra from source code, please pull the latest source from github : https://github.com/Hydra-Chain/node
The instruction for compilation : https://github.com/Hydra-Chain/node Currently we recommend to compile on Linux or OSX, while other platforms might need more configuration.
After compilation, you also get hydrad and hydra-cli under the path/src/
3. Get Hydra node docker image
Suppose user has docker environment installed correctly. (what is docker?)
The Hydra official docker image on docker hub is locktrip/hydra-node, you can pull it by docker command :
docker run -d -P --name Hydra -v /src/hydra:/hydra -e TZ=Europe/Sofia -i -t -p 3338:3338 locktrip/hydra-node
Make sure to set your time zone according to your locale. Startup flags can be set as well such as -staking=false to disable staking.
https://hub.docker.com/r/locktrip/hydra-node
All the ways above can get Hydra nodes. There are two important binaries which are related to deployment and RPC calls:
hydrad:Hydra core program, i.e. Hydra fullnode program.
hydra-cli:Hydra command line interface,interact with hydrad, achieve RPC calls.
Deploy Hydra node
For the instruction for Hydra docker images, please refer to "How to launch Hydra with docker".
Other normal deployment methods are almost the same, here we take Ubuntu as an example. The commands in Mac and windows are exactly the same.
Run Hydra fullnode with ./hydrad:
This with launch a hydrad daemon with the option -daemon. If user are interested in the event logs about smart contract, please add one more option -logevents.
More options can be found:
To stop running:
The default data path for different platforms:
Linux:
~/.hydraMac OSX:
~/Library/Application Support/hydraWindows:
%APPDATA%\hydra
You can also use -datadir to set your own data path。
hydra node will sync all the historical block data for first launch, and saves to datadir. It might take some time. Then diagnostics for the node can be found under the data path ~/.hydra/debug.log。
Local RPC call
When the hydra node is running, we can use hydra command line interface hydra-cli to interact with hydrad, and make local RPC calls.
e.g.:
To get all RPC command list:
To get help for specific RPC command, use ./hydra-cli help,e.g.:
JsonRPC settings
You can get the jsonrpc example by using (here we use getinfo as an example): ./hydra-cli help getinfo
The example shows detailed format for jsonrpc content. However, it can only be called after setting rpcuser and rpcpassword. There are two ways to set the parameters, you can choose either.
Method 1:Create config file ~/.hydra/hydra.conf,which should include:
For more config settings, please refer to :hydra.conf example
After creating the config file, please restart the node to finish settings.
Method 2:Restart Hydra node with following options:
The meaning of options rpcuser, rpcpassword and rpcallowip are all the same with the config file above.
RPC call example
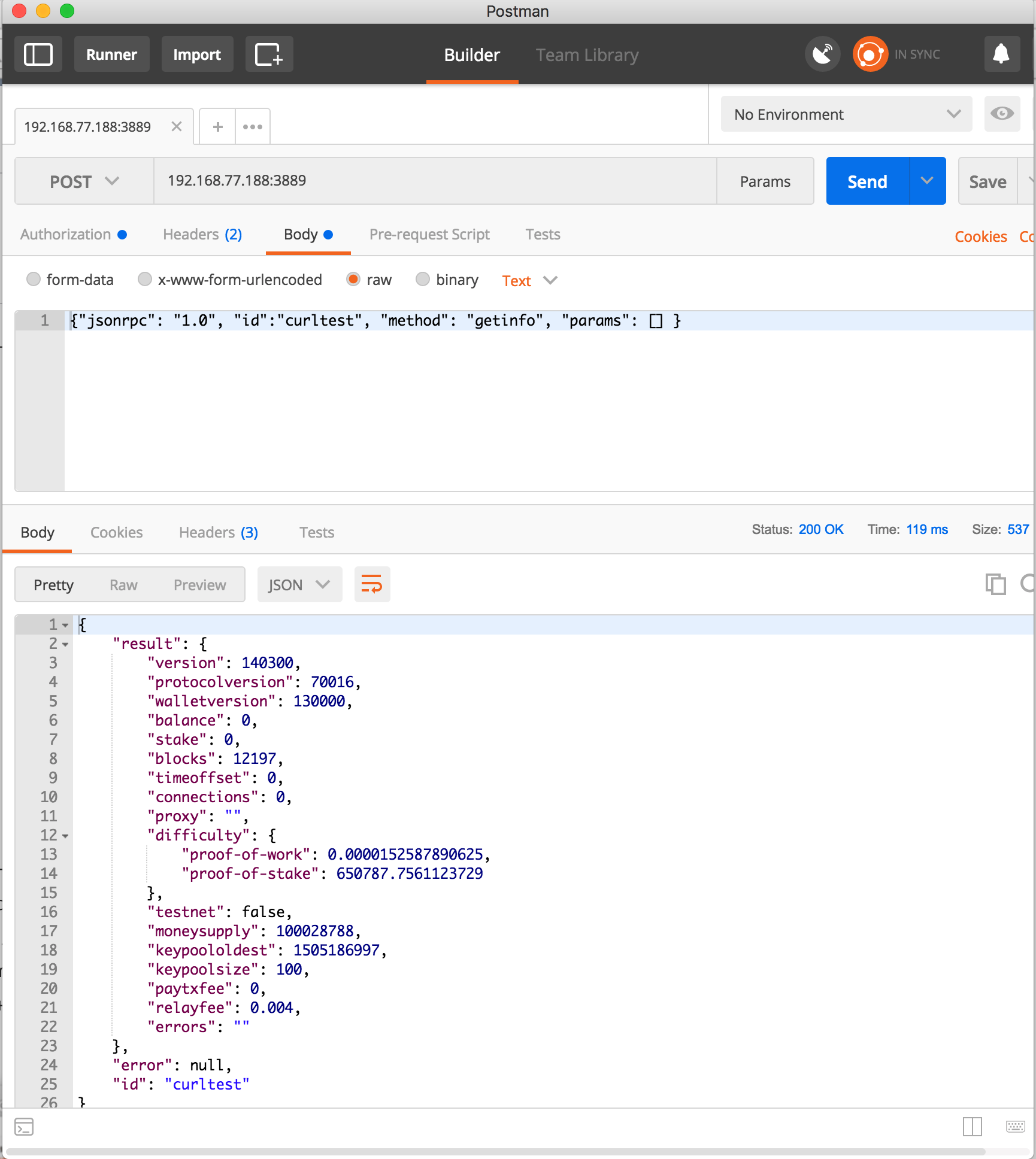
You can make remote RPC calls after the settings above. Here is an example: Suppose the hydra node is running on an Ubuntu machine, whose ip is 192.168.77.188, default port=3389. Now we try to make jsonrpc call in a remote macbook:
The result is identical with local call.
You can also use tools like postman to get the same result:
Nginx settings(optional)
As the example above, you might find that it is quite complicated to make remote jsonrpc, since you must include rpcuser, rpcpassword, as well as port in the command. If you don't want users to provide these parameters, we recommand using Nginx. The benefits for Nginx is not only about simplification, but also a good way to hide rpcuser, rpcpassword and port number. And you can filter some RPCs for security. Here we suppose the reader have installed Nginx and have basic knowledges about how to use it.
example:
hydra node is running on
192.168.77.188,api proxy ip
192.168.77.51, with Nginx installed
Instructions:
1.Set the hydra.conf of hydra node, remember to add the proxy ip to rpcallowip e.g.:
2.Setup Nginx :
3.Then you can make remote rpc call through proxy, without rpcuser or rpcpassword. e.g.:
This is only a simple example. You might have different settings or tools instead.
Executing common commands through RPC (create wallet,transfer amount and get balance)
CREATEWALLET
Creates and loads a new wallet.
Arguments:
Result:
Examples:
Test example:
Test result:
TRANSFER AMOUNT
Send an amount to a given address.
Requires wallet passphrase to be set with walletpassphrase call.
Arguments:
Result:
Examples:
GETBALANCE
Returns the total available balance. The available balance is what the wallet considers currently spendable, and is thus affected by options which limit spendability such as -spendzeroconfchange.
Arguments:
Result:
Examples:
As a json RPC call:
Test example:
Test result:
If you have any questions during node deployment and RPC calls, here are some useful documents to refer to:
For source code compilation issues:
https://github.com/Hydra-Chain/node
Command to check all hydrad options:
./hydrad -helpCommand to get all RPC list:
./hydra-cli helpGet RPC help(like getinfo):
./hydra-cli help getinfohydra.conf file example:hydra.conf
Last updated
Was this helpful?